The Rubber Story
A Balancing Act Between Growth and Sustainability
10th December 2023

Natural rubber is a fantastic material with a fascinating story that spans centuries. It all starts in Southeast Asia’s rainforests, where the sap of the Hevea brasiliensis tree, called latex, is the key to creating this versatile material. From ancient times to modern industries, the story of rubber is one of resilience, innovation, and a continuous evolution with profound impacts on the world around us.
Indigenous cultures have long used rubber for various purposes, from making waterproof boots to crafting decorative objects. When European explorers arrived in the 15th century, they were amazed by rubber’s unique properties and started exploring its potential. This led to the development of new processing techniques, paving the way for the widespread use of rubber in various industries.
In the 19th century, the rubber industry revolutionized with Charles Goodyear’s invention of vulcanization. This process transformed rubber, making it more durable and resistant to heat and cold, unlocking its vast potential for countless applications. This marked the beginning of the modern rubber age, leading to rapid technological advancement and industrial growth.
Rubber has had a profound impact on society, from revolutionizing transportation with bicycle tyres to protecting healthcare workers with life-saving medical gloves. Today, its uses extend far beyond tyres and gloves, permeating countless industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and even electronics.
However, the rubber industry faces challenges related to environmental sustainability and ethical sourcing. Balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility is crucial to ensure a sustainable future for natural rubber and the communities that depend on it.
As we move forward, the story of rubber continues to unfold. Emerging technologies are pushing innovation boundaries and exploring new applications for this remarkable material. The journey from the rainforest to our everyday lives is a testament to humanity’s ingenuity and nature’s potential to provide for our needs and aspirations. It is a story that is full of history, innovation, and a promise of a brighter future. This reminds us of the remarkable journey from the humble Hevea tree to the countless ways rubber shapes our world. Let’s understand the rubber story in the new age of sustainability.
The World of Natural Rubber: A Balancing Act Between Growth and Sustainability
Natural rubber, a prized elastomer derived from the sap of the Hevea brasiliensis tree, is an indispensable resource in countless industries, from automotive and tyre manufacturing to medical equipment and consumer goods. Yet, as global demand for this versatile material continues to surge, the industry finds itself at a critical juncture, grappling with the challenges of balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability.
A Booming Industry with Global Reach
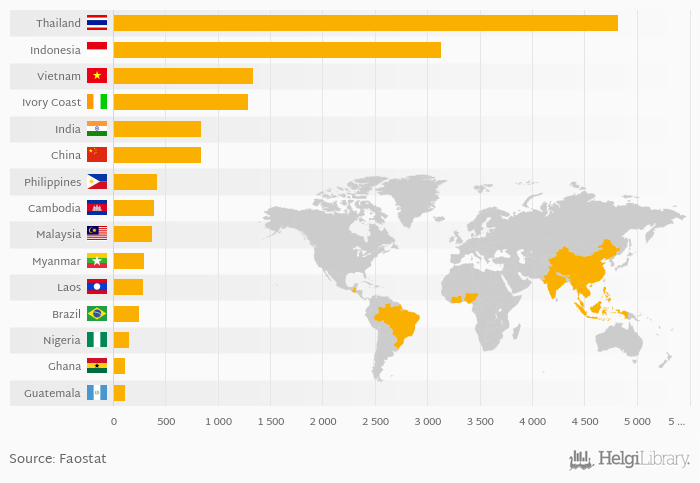
Natural rubber production is a global endeavor, with Southeast Asia serving as the epicenter. A handful of nations dominate the scene, producing the vast majority of the world’s natural rubber:
- Thailand: As the undisputed leader, Thailand boasts an annual production of approximately 4.5 million metric tons of natural rubber (2022 data). Smallholder farmers, who own and manage relatively small plots of land, play a pivotal role in the country’s rubber industry.
- Indonesia: Following closely behind Thailand, Indonesia churns out around 3.5 million metric tons of natural rubber annually (2022 data). Unlike Thailand, Indonesia’s rubber production is characterized by large-scale estates owned by corporations and governments.
- Vietnam: Emerging as a rising star, Vietnam has witnessed remarkable growth in its natural rubber production, reaching 1.2 million metric tons in 2022. Government initiatives and increasing domestic demand for rubber products have fueled this expansion.
- India: India contributes significantly to the global supply with an annual production of around 0.8 million metric tons (2022 data). Smallholder farmers are the backbone of India’s rubber industry, primarily concentrated in the southern states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- Malaysia: Completing the top five, Malaysia produces approximately 0.7 million metric tons of natural rubber annually (2022 data). Malaysia’s rubber industry has a long and storied history, dating back to the colonial era.
Beyond the Top Five
While these five nations account for the lion’s share of global production, other countries, including China, Ivory Coast, and the Philippines, also contribute to the natural rubber supply chain. Each nation has its own unique production landscape, ranging from smallholder farms to large plantations.
The Path to Sustainability
The growing demand for natural rubber has raised concerns about deforestation, biodiversity loss, and the environmental impact of rubber cultivation. To address these challenges, the industry is exploring a range of sustainable practices, such as:
- Agroforestry: Integrating rubber trees with other crops and trees to promote biodiversity and soil health.
- Responsible Land Use: Avoiding deforestation and land conversion for new rubber plantations.
- Improved Farming Practices: Implementing techniques that reduce water consumption, minimize pesticide use, and enhance soil fertility.
- Fair Trade and Labor Rights: Ensuring fair wages and working conditions for rubber farmers and workers.
The future of natural rubber depends on a delicate balancing act between meeting growing demand and ensuring environmental sustainability. By embracing innovative and responsible practices, the industry can continue to thrive while minimizing its ecological footprint.
For further information on natural rubber production and sustainability efforts, you can refer to resources such as:
- The International Rubber Study Group (IRSG): https://www.rubberstudy.com/
- The Sustainable Natural Rubber Initiative (SNR): https://sustainablenaturalrubber.org/
- By working together, stakeholders across the natural rubber value chain can ensure a sustainable and prosperous future for this invaluable resource.

The Natural Rubber Market size is expected to grow from USD 17.33 billion in 2023 to USD 21.80 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 4.70% during the forecast period (2023-2028).
The market is segmented by type (natural rubber and synthetic rubber) and application (automotive, tyres, medical, industrial, consumer goods, and others). Currently, the automotive sector is the largest consumer of rubber, followed by the tyre industry.
A Material of Many Uses:
The applications of natural rubber are diverse and far-reaching. Tyres, the most significant consumers, utilize natural rubber for its superior elasticity, durability, and resistance to rolling. Beyond tyres, the medical industry relies on natural rubber for gloves, catheters, and other essential equipment. Natural rubber permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from industrial belts and hoses to sporting goods and footwear.
Sustainability Concerns and the Drive for Change
While natural rubber’s benefits are undeniable, its production’s environmental impact raises serious concerns. Traditional cultivation practices often involve deforestation, soil erosion, and pollution from fertilizers and pesticides. Additionally, the industry faces challenges from climate change, with threats from changing weather patterns and increased disease outbreaks.
Embracing Sustainability:
Recognizing the need for change, the natural rubber industry actively embraces sustainability practices. This includes:
- Improved cultivation techniques: Sustainable farming methods promote biodiversity, reduce deforestation, and minimize the use of harmful chemicals.
- Certification schemes: Programs like the Roundtable on Sustainable Natural Rubber (RSNR) and the International Rubber Consortium (IRCoC) promote responsible and transparent practices throughout the supply chain.
- Research and development: Investments in research aim to develop high-yielding, disease-resistant rubber varieties and explore alternative sources of natural rubber.
Regulations like the EUDR:
The European Union’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) is a landmark legislation that aims to combat deforestation associated with imported commodities, including natural rubber. This regulation requires companies to ensure their products are deforestation-free, placing pressure on the industry to adopt more sustainable practices.
Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
The road to sustainability in the natural rubber industry is paved with challenges and opportunities.
Challenges:
- Balancing growth with sustainability: Meeting the increasing demand for natural rubber requires careful management to ensure sustainable practices are not compromised.
- Smallholder farmers: Supporting smallholder farmers, who comprise a significant portion of the industry, in adopting sustainable practices is crucial for long-term success.
- Monitoring and enforcement: Effective monitoring and enforcement mechanisms are essential to ensure compliance with sustainability standards.
Opportunities:
- Technological advancements: Innovations in precision agriculture, Satellite data, Deforestation, Data Provenance, use of big data in Supply chain further improve sustainability practices.
- Consumer demand: Growing consumer awareness and demand for sustainable products can incentivize companies to adopt responsible practices.
- Emerging markets: Expanding demand from emerging markets presents opportunities for sustainable rubber production.
A Sustainable Future for Natural Rubber
The future of natural rubber lies in striking a delicate balance between growth and sustainability. By embracing responsible practices, investing in innovation, and fostering collaboration, the industry can ensure a sustainable future for this essential material while protecting the environment for future generations.

The future of natural rubber is bright, but it requires collective effort and a commitment to sustainability from all stakeholders.
Expanding on the Initiatives of Michelin Group, Continental AG, IRCoC, GPSNR, Rainforest Alliance, ATMA and TRST01:
Michelin Group:
- Michelin Development Program: This program provides technical assistance and training to smallholder farmers in Indonesia on sustainable practices such as agroforestry, composting, and soil conservation.
- Livelihood Improvement Project: This project supports the economic development of rubber-growing communities in Indonesia through microfinance programs, healthcare initiatives, and educational support.
- Rubberway App: This innovative app allows Michelin to map and assess the sustainability practices of rubber plantations throughout its supply chain, promoting transparency and accountability.
Continental AG:
- Sustainable Natural Rubber Policy: Continental has established a comprehensive policy outlining its commitment to sourcing deforestation-free natural rubber and promoting responsible practices throughout its supply chain.
- Partnership with WWF: Continental collaborates with WWF to develop traceability systems and implement sustainable farming practices in rubber plantations across Southeast Asia.
- Investment in Research: Continental actively supports research initiatives to develop high-yielding, disease-resistant rubber varieties and explore alternative sources of natural rubber.
International Rubber Consortium (IRCoC):
- Multi-stakeholder platform: IRCoC facilitates dialogue and collaboration between governments, NGOs, industry players, and smallholder farmers to address sustainability challenges in the natural rubber industry.
- Knowledge sharing and capacity building: IRCoC organizes workshops, training programs, and knowledge-sharing initiatives to promote best practices in sustainable rubber production among smallholder farmers.
- Development of sustainability guidelines: IRCoC works with stakeholders to develop and implement sustainability guidelines for the natural rubber industry, covering aspects like environmental protection, social responsibility, and economic viability.
Global Platform for Sustainable Natural Rubber (GPSNR):
- Standard setting: GPSNR develops and implements global standards for sustainable natural rubber production, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain.
- Monitoring and evaluation: GPSNR monitors progress towards sustainability goals and identifies areas for improvement through data collection and analysis.
- Promoting innovation: GPSNR fosters research and development initiatives to advance sustainable practices in the natural rubber industry.
Rainforest Alliance:
- Sustainable Agriculture Network (SAN): Rainforest Alliance works with rubber producers to implement the SAN standard, which promotes environmentally responsible practices, social justice, and economic viability.
- Forest conservation: Rain Forest Alliance works to protect critical ecosystems and promote sustainable land management practices in rubber-growing regions.
- Community engagement: Rainforest Alliance actively engages with local communities to promote social and economic development in rubber-producing regions.
ATMA
The Automotive Tyre Manufacturers Association is the apex body of the Indian Tyre Industry. It promotes sustainable growth and development in the industry through various initiatives, including:
- Using environmentally friendly materials: ATMA encourages using natural rubber, recycled rubber, and bio-based materials in tyre production.
- Reducing environmental impact: ATMA supports tyre manufacturers in reducing water and energy consumption and minimizing waste generation.
- Promoting tyre recycling: ATMA encourages retreading, recycling, and using tyres as fuel sources for sustainable end-of-life management.
- Responsible sourcing: ATMA advocates for sourcing raw materials from certified sources like the Roundtable on Sustainable Natural Rubber.
ATMA’s initiatives have demonstrably improved the environmental performance of the Indian Tyre Industry, significantly reducing energy consumption, water usage, and emissions. Their commitment to sustainability is evident in their vision of a globally competitive industry contributing to economic growth while ensuring environmental and social well-being. Their work aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and they have been recognized for their leadership by the Indian government and international organizations. Transparency and Sustainability in the Natural Rubber Industry.
These initiatives highlight the diverse approaches taken by various stakeholders to address the sustainability challenges in the natural rubber industry. By collaborating and sharing best practices, these organizations are paving the way for a more sustainable future for natural rubber, ensuring its continued availability for future generations.
It is important to note that these initiatives are just a few examples of the ongoing efforts towards sustainable natural rubber. Many other organizations and individuals actively promote responsible practices and protecting the environment. Ultimately, the success of these efforts depends on the continued commitment and collaboration of all stakeholders throughout the natural rubber supply chain.

Enhancing Transparency and Sustainability in the Natural Rubber Industry
TRST01Chain significantly enhances traceability and transparency within the rubber supply chain, enabling exporters to authenticate and certify that their products comply with essential environmental and quality standards. Additionally, TRST01Chain meets the Due Diligence Requirements of the European Union’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) under specific country legal frameworks. With TRST01Chain solutions deployed across over a million hectares of rubber plantations in countries like India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, Thailand, Ivory Coast, China, Laos, and Côte d’Ivoire, the system plays a crucial role in global rubber supply chain management.
By integrating TRST01Chain into their operations, Indian rubber exporters ensure continued access to vital markets, particularly in Europe where stringent compliance regulations often serve as significant barriers to entry. This technology not only helps protect the global reputation of Indian rubber but also boosts operational efficiency for exporters by mitigating risks associated with compliance failures and market access disruptions.
The natural rubber industry confronts severe challenges related to transparency, counterfeiting, and inefficiency. Addressing these issues demands innovative solutions that promote sustainability and protect consumers. TRST01 provides a secure platform designed for enhancing supply chain traceability, offering a promising application in the natural rubber industry. By furnishing an immutable record of a product’s journey from farm to finished product, TRST01 enhances transparency and accountability across the supply chain. This improved visibility aids in identifying and mitigating environmental and social risks, ensuring responsible sourcing practices and sustainable production. Moreover, the platform’s robust infrastructure combats counterfeit rubber products, safeguarding brand integrity and consumer safety.
While challenges such as scalability, data integration, and user adoption persist, TRST01’s potential to improve transparency and sustainability in the natural rubber industry is substantial. Collaboration among technology providers, industry stakeholders, and policymakers is essential to navigate these challenges and fully leverage the platform’s capabilities. By adopting innovative solutions like TRST01, the natural rubber industry can progress towards a more responsible and sustainable future.
Sources
General information:
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): https://www.fao.org/3/ad452e/ad452e2c.htm
- International Rubber Study Group (IRSG): https://www.rubberstudy.org/
- World Rubber Industry Report (WRIR): https://rubberworld.com/market-reports/
- Natural Rubber News: https://www.rubbernews.com/
Sustainability and regulations:
- Roundtable on Sustainable Natural Rubber (RSNR): https://sustainableroundtable.org/
- International Rubber Consortium (IRCoC): https://ircorubber.com/
- European Union’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR):https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/forests/deforestation/regulation-deforestation-free-products_en
Specific examples of sustainability initiatives:
- Michelin Group: https://natural-rubber.michelin.com/
- Continental AG: https://www.continental.com/en/press/press-releases/20220928-responsible-sourcing-of-natural-rubber/
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF): https://www.worldwildlife.org/initiatives
Additional resources:
- The Nature Conservancy: https://www.nature.org/en-us/
- Rainforest Alliance: https://www.rainforest-alliance.org/
Other relevant reports and articles:
The Future of Natural Rubber: Challenges and Opportunities” by the International Rubber Research Institute (IRRDB): https://www.informaconnect.com.sg/insight/transforming-challenges-opportunities-natural-rubber-industry/
- Sustainable Natural Rubber: A Guide for Businesses” by WWF: https://www.worldwildlife.org/blog-posts/wwf-to-the-natural-rubber-sector-time-to-put-the-pedal-to-the-metal
- Natural Rubber: A Review of Sustainability Issues and Initiatives” by the Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR): https://forestsnews.cifor.org/78076/huge-potential-for-sustainability-with-natural-rubber-experts-say?fnl=
Recent Comments
Recent Posts
- Driving Global Impact: Regulation, Technology, and Adoption July 14, 2024
- Blockchain Revolutionising Provenance Global Supply Chains July 11, 2024
- Supply Chain Innovation TRST01Chain June 18, 2024
- Blockchain for Sustainability June 14, 2024
- EUDR Coffee : Between the Cup and the Lip June 9, 2024
- EUDR and India Rubber Export May 25, 2024
- Data Driven Sustainability April 28, 2024
- Paradigm Shift in ESG April 14, 2024
- ESG Beyond the Reports March 21, 2024
- The Kenko Eggs A Case Study February 18, 2024
- New Frontier : Carbon Broader Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) January 27, 2024
- Sustainable Transformation Future ESG Management January 21, 2024
- EUDR Compliance in Indian Trade January 7, 2024
- The Indian Coffee Story : Brewing Harmony December 16, 2023
- The Rubber Story : Between Growth and Sustainability December 10, 2023
- The 4R Strategy : Roadmap to Sustainable Growth December 3, 2023
- Sustainable Indian Coffee: A EUDR Perspective November 10, 2023
- Climate Tech and SDGs: Unlocking Potential October 21, 2023
- ESG Scorecards : TRST01’s Vision October 11, 2023
- The Imperative of Carbon Accounting October 8, 2023
- TRST01Chain on International Coffee Day October 1, 2023
- Footprint Lite – Embracing SME September 24, 2023
- Footprint ESG – Embracing Enterprise September 14, 2023
- Empowering Tomorrow: Innovation, Pivoting, and Sustainability at TRST01 August 27, 2023
- TRST01Chain for Scope 3 Reporting August 12, 2023




