Climate Tech and SDGs
TRST01: Unleashing Climate Tech Potential in Harmony with SDGs
21th October 2023
Contributor Shiva Shanker, Head Sustainability TRST01

Introduction
In 2015, the United Nations adopted a visionary blueprint for global development, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These 17 interconnected goals encompass social, economic, and environmental dimensions, with SDG 13, “Climate Action,” standing out as a top priority. It underscores the urgency of addressing climate change and its profound consequences. In this context, aligning climate tech innovations with the SDGs isn’t merely a matter of technological advancement; it’s a necessity for achieving sustainable development.
Climate Tech: A Catalyst for Change
Climate tech represents diverse, innovative technologies to mitigate and adapt to climate change. From renewable energy solutions and carbon capture technologies to sustainable agriculture practices and climate-resilient infrastructure, climate tech offers a comprehensive toolkit for tackling the climate crisis head-on.
SDG Alignment: A Shared Vision
The alignment of climate tech innovations with the SDGs creates a powerful synergy. It ensures that technological advancements are directed towards achieving broader sustainability goals, fostering a holistic approach to climate action. Recognizing that climate change is intricately linked with other development challenges such as poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation, this alignment reinforces our commitment to address these multifaceted issues.
Unlocking the Potential

Accelerated Progress
Footprint By TRST01
Aligning climate technology innovations with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) can expedite progress towards achieving these global objectives. Climate technology solutions, also known as clean technology or cleantech, are designed to reduce the negative Impact of human activities on the environment while promoting sustainable growth. These technologies are often efficient, scalable, and impactful, making them an essential tool for achieving the SDGs.
One example of how climate tech can help achieve multiple SDGs is the widespread adoption of renewable energy technologies such as solar and wind power. These technologies can provide clean and affordable energy (SDG 7) while reducing carbon emissions, contributing to climate change. In addition, adopting renewable energy technologies can create new job opportunities, supporting the goal of promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all (SDG 8).
Furthermore, measuring an organization’s carbon footprint is essential in Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) reporting. Carbon footprint measures the amount of greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide, emitted during the production, use, and disposal of goods and services. Tools such as Footprint by TRST01 deploy robust Scope 1, 2, and 3 calculators to accurately measure an organization’s carbon footprint. By measuring their carbon footprint, organizations can identify areas to reduce emissions and effectively manage their environmental Impact.
The Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR) framework is based on the National Guidelines on Responsible Business Conduct (NGRBC), which the Indian government developed in alignment with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The NGRBC principles are closely linked to the 17 SDGs, providing a comprehensive framework for responsible business practices. Under the BRSR framework, organizations are required to disclose their performance relative to these principles, including their progress towards achieving the SDGs. This framework helps ensure that businesses are accountable for their Impact on the environment and society and promotes responsible business practices.

Shared Solutions
TRST01Chain
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of targets established by the United Nations to promote sustainable development and address global challenges. The alignment of these goals encourages the creation of sustainable and innovative climate technology solutions that can handle multiple objectives simultaneously, fostering integrated and cross-cutting approaches.
One great example of this is the development of intelligent and sustainable cities (SDG 11), which can reduce emissions, enhance public transportation (SDG 9), and improve air quality (SDG 3). Integrating technology into cities can help improve the efficiency and effectiveness of services, reduce waste, and promote sustainable practices.
TRST01Chain’s sustainable supply chain traceability solution is a critical instrument in alignment with the SDGs. This innovative solution promotes ethical sourcing, empowers farmers, and fosters transparency throughout the supply chain. By doing so, it contributes significantly to multiple SDGs.
For instance, it empowers farmers, potentially improving their incomes and market access (SDG 1) while promoting sustainable agriculture and food security (SDG 2). It supports fair labor practices and sustainable economic growth (SDG 8) while encouraging responsible consumption and production (SDG 12). Moreover, it embodies the spirit of collaboration and partnerships, aligning with SDG 17’s emphasis on collective efforts for sustainable development.
TRST01Chain’s traceability system includes farmer demographic data capture, ethical sourcing tracking, sustainability certifications, and enhanced consumer engagement, all of which align with these SDGs. By doing so, it contributes to building a more sustainable, equitable, and transparent global food system. This innovative solution enables consumers to make informed decisions about the products they purchase, promoting transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. It also empowers farmers, promoting their socio-economic well-being and aligning with the SDGs’ objectives of reducing poverty and inequality, promoting sustainable agriculture, and ensuring responsible consumption and production.
Enhanced Impact
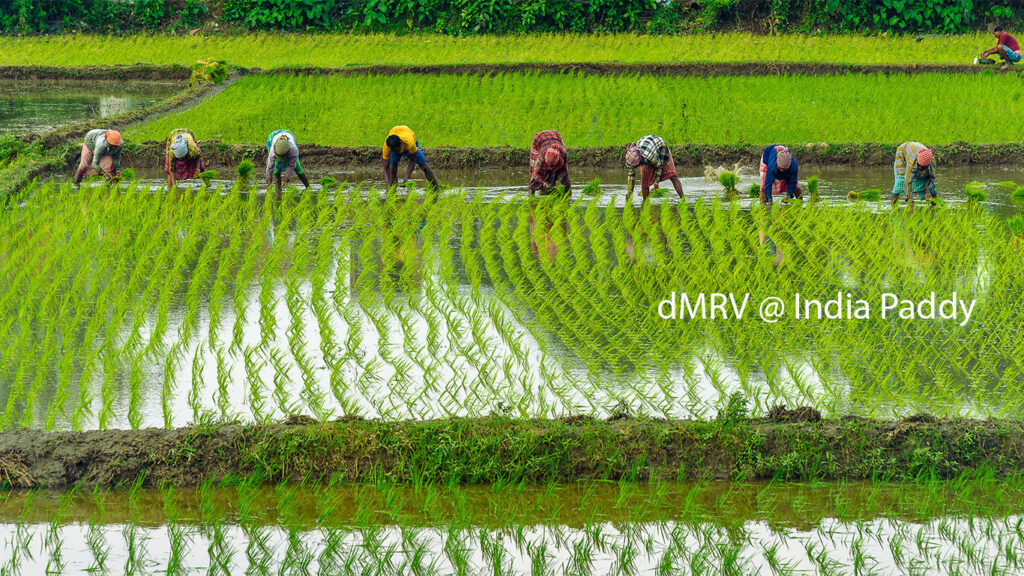
dMRV by TRST01
In order for climate technology to be truly effective, it must address not only the environmental impacts of climate change but also the social and economic dimensions of this global challenge. By aligning climate tech with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), we can ensure that innovations in this field promote comprehensive and integrated solutions that benefit society as a whole.
One example of such innovation is TRST01’s digital solution for measuring, reporting, and verifying (dMRV) climate-positive actions. This technology aligns with the SDGs in multiple ways, providing a comprehensive approach to climate action that incorporates greenhouse gas emissions reductions, carbon sequestration, and positive climate impacts. By measuring a range of impacts, dMRV reflects the SDGs’ integrated solutions focus, which recognizes that environmental, social, and economic goals are all interconnected.
In addition to its comprehensive approach, dMRV also incorporates SDG-specific indicators to evaluate climate action within the context of broader sustainability goals. This promotes transparency and accountability, ensuring that climate action is not pursued at the expense of other important societal objectives.
Moreover, dMRV encourages inclusive participation, which aligns with the SDG principle of inclusivity. By engaging a wide range of stakeholders in the climate action process, dMRV helps to ensure that climate solutions are equitable and effective for all members of society.
Finally, dMRV goes beyond mere reporting by linking climate action data to real-world impacts. For example, it measures the effect of climate-smart agricultural practices on poverty reduction (SDG 1), tracks sustainable agriculture practices for food security (SDG 2), measures greenhouse gas reductions for climate action (SDG 13), and assesses biodiversity conservation for life on land (SDG 15). By connecting climate action to these broader societal goals, dMRV ensures that climate solutions contribute meaningfully to a more sustainable and equitable future for all.

Fostering Collaboration
Identifying Priority Areas:
Collaborative efforts should begin by identifying the SDG targets where climate tech can have the most significant Impact. This requires comprehensive analysis and dialogue among stakeholders. Governments, businesses, and civil society organizations can work together to prioritize specific areas of intervention. For example, stakeholders might prioritize clean energy solutions in regions heavily reliant on fossil fuels, aligning with SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
Directing Investments:
To harness the full potential of climate technology, it is crucial to invest and distribute funds strategically. Collaborative efforts between governments and private sector organizations can facilitate the allocation of resources towards climate technology innovations that align with specific SDG targets. By making a financial commitment, we can speed up the research, development, and deployment of climate technology. For example, partnerships between governments and renewable energy companies can help increase the production of clean energy in line with SDG 7.
Promoting Knowledge Sharing:
Collaboration thrives on the exchange of knowledge and expertise. Facilitating knowledge sharing among stakeholders is essential for accelerating innovation and deploying climate tech solutions. Research institutions, academia, and industry leaders can create platforms for sharing best practices, data, and research findings. By fostering open communication, we can collectively learn from successes and failures, driving continuous improvement in climate tech innovations.
Engaging Civil Society:
Collaboration isn’t limited to governments and businesses. Civil society organizations, non-profits, and grassroots movements are crucial in advocating for climate action and holding stakeholders accountable. Collaboration with these groups can amplify the Impact of climate tech initiatives and ensure that they address the needs and concerns of local communities, aligning with SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
Conclusion
Aligning climate tech innovations with the SDGs is not merely a strategic choice; it’s a moral imperative. By harnessing the power of technology and aligning it with the global sustainability agenda, we can pave the way for a future where climate action and sustainable development walk hand in hand. This alignment promises a brighter, more resilient future for all, where we actively contribute to a just, equitable, and sustainable world. In this journey, our actions speak louder than words, shaping the world we aspire to leave for future generations.