Knowledge Share
New Normal, Digital Transformation, Industry 4.0
Trust | Transparency | Traceability
Vaccine and BlockChain

In India, the Covid-19 vaccine will be directly procured by the Central Government and distributed among the priority groups free of cost under a unique immunisation programme. It contains four categories of people – healthcare professionals including doctors, nurses and ASHA workers, frontline workers, including Anganwadi workers, sanitation workers, police personnel and armed forces. Generally, the process of developing drugs and vaccines is lengthy and expensive, often associated with high costs and high failure rates. On an average, it takes initially 5 to 15 years for a vaccine or drugs to launch in the market with an expensive process to costs around $800M – $2.5B per drug at a high-risk level of being viable in the market (at the success rate of 1 in 5 drugs to be market-ready; and only 1 in 3 drugs to be profitable).
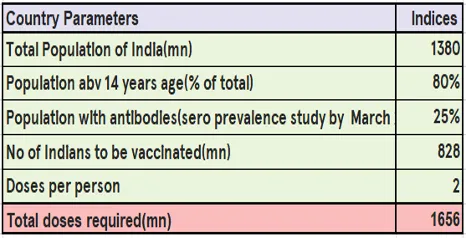 What is the Issue: the Year 2019, it is estimated 25% of vaccines degraded by the time they arrive at their destination. Research suggests that these vaccines won’t cause any adverse effects, but could offer decreased protection and might require patients to revaccinated. This is mainly due to the inappropriate shipping procedures in the cold supply chain, which results in a loss of US$34.1 billion annually. Experts estimate that for the pandemics, the doses of vaccine required could range somewhere between 12 billion and 15 billion, which require fewer events of fallacy in order to be properly utilised and scaled economically.
What is the Issue: the Year 2019, it is estimated 25% of vaccines degraded by the time they arrive at their destination. Research suggests that these vaccines won’t cause any adverse effects, but could offer decreased protection and might require patients to revaccinated. This is mainly due to the inappropriate shipping procedures in the cold supply chain, which results in a loss of US$34.1 billion annually. Experts estimate that for the pandemics, the doses of vaccine required could range somewhere between 12 billion and 15 billion, which require fewer events of fallacy in order to be properly utilised and scaled economically.
Point to ponder: How can recipients of the vaccine rest assured that their vaccines have not been compromised by faulty storage handling, putting recipients and their surrounding social environment at risk? Is it possible to monitor and verify the proper storage of the vaccine?
Solution: The answer could lie in the use of emerging technology or Blockchain to be precise, which could result in a new era for vaccines and vaccinology. The COVID-19 vaccine through different phases in the market fast-tracked to an occurrence of within a year, represents technological innovation at its best.
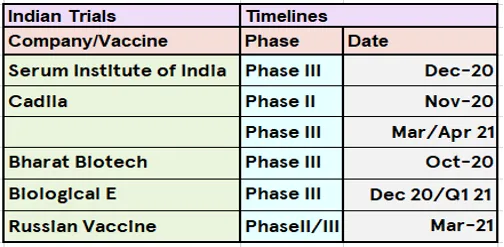
What’s next: In terms of discovery: As mRNA technology improves, so should the speed at which the new vaccines can be developed or rolled out, which would be hugely beneficial when the inevitable next pandemic hits.
What’s next: In terms of distribution: Blockchain tech is ideal for SARS-CoV-2 vaccine supply chains according to experts because of its imbibed properties of efficiency and trust.
Quality assurance and preventing counterfeits: A chain of custody will need to be maintained from cradle-to-grave – to ensure a verifiable transcript of the vaccine’s lifecycle and journey. And to that traceability is a must, considering a long history of counterfeiting in pharmaceutical supply chains. It is also to be noted that distributing vaccines to just about everyone on the globe has also never been attempted before. Unfortunately, there’s no gene-based shortcut for the hard work of logistics. As Bill Gates, in its recent interview, stated “it is not necessary to provide vaccines to everyone. We must prioritise among the essentials and vulnerable group and then scale accordingly.
ETgarage solution BlockiT256 leverages on new technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence, and Blockchain to track all product in the supply chain and gather data about each product. Access to such data helps in preventing failures of distribution, predicting the demand and capacity levels, and reducing the cost and wastage of all limited resources.

Trust in a system is very important, especially in vaccines and henceforth the breakthroughs in emerging technology have led the pathway for gaining trust and authenticity, especially to the sector of pharma and life sciences.

Share Blog on: