Knowledge Share
New Normal, Digital Transformation, Industry 4.0
Trust | Transparency | Traceability
Retail Banking on Blockchain

India’s retail loan assets are forecasted to grow to $3 trillion by 2026. As digitisation accelerates, the battle to acquire customers for banks is expected to tighten up with peer-to-peer lenders and FinTech startups. In 2019-20, the total transaction value in the digital payment segment was more than $69 billion and grew 24% year on year. The retail banking sector is exploring Blockchain technology as a viable option to harness this capability. Transparency, Governance, and Accountability are the most sought features that Blockchain provides by design, and according to reports by 2022, This to save banks $20 billion per year in infrastructure costs.
Blockchain has brought a dramatic change to the banking channels in the last few years and is considered a potential new revolution for the retail banking space. In due course of time, the Banking industry accounts for 30 % of total blockchain spending by 2023. Nowadays, the retail banking sector is characterised by multiple products on deposits, credit, insurance, investments and securities; numerous channels of distribution via branch or internet; and multiple customer groups including consumer, small business, and corporate. In India, retail lenders traditionally relied on in-person interactions during the lifecycle of the loan process, right from sourcing to disbursal. But with the passage of time and advent of technology, retail banks have been more focused upon the following
- Developing a customer-centric business model
- Optimising distribution
- Simplifying business and operating models
- Obtaining an information advantage
- Enabling innovation and the capabilities
- Proactively managing risk, regulations and capital
Using immutable smart contracts, borrowers can directly deal with the lenders on the interest rate, instalments, and duration of the transaction. Data like KYC, credit scores, profiling data, account types, relationship data, business profiles, structured and unstructured data, and other social media data held across multiple member institutions might be combined to make far better, secure, and accurate profiling a credit approval decision. And therefore, Blockchain has the potential to distribute more value than wealth.
The Blockchain is considered as the Internet of Value, and the process of TRST01 is easy to integrate with original process flow in a straightforward, secure and transparent framework through the following procedures
- To understand bank and its business
- To study the “As-Is” State, of the process and flows of transactions
- To map pain-points to process improvement
- To research and recommend the Blockchain patented integration technology
- To layout and define future state processes
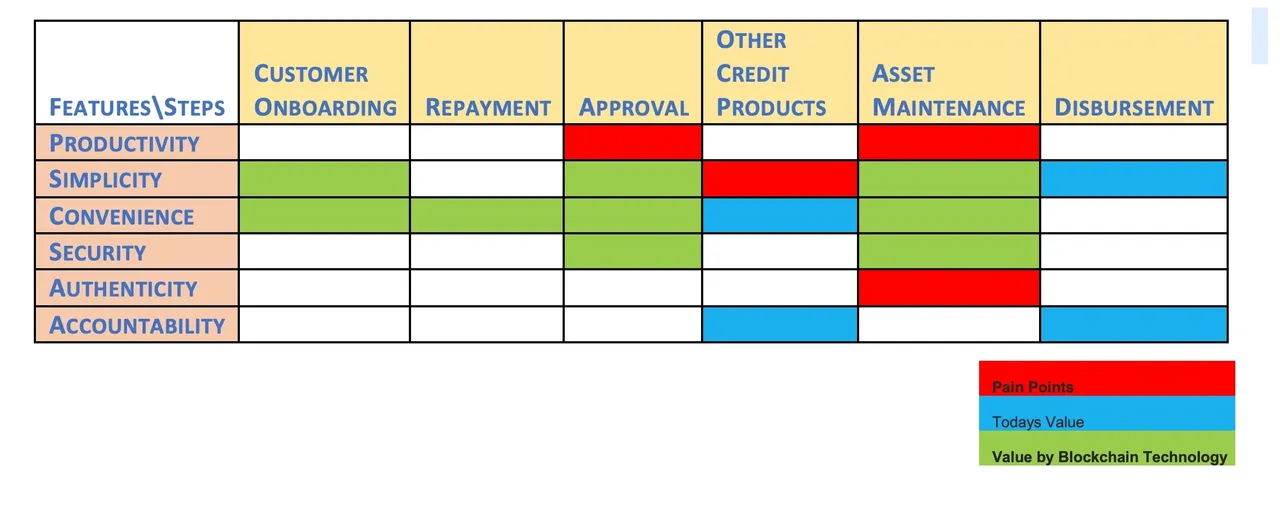
The general buyer utility INDEX CAN therefore BE COMPREHENDED with the following MATRIX
Reference
Share Blog on: